Python和MATLAB的协同使用
最近科研中需要联合使用Python和MATLAB,所以写下这篇博客记录一下中间踩坑的历程,也希望能对后续的有相同疑惑的同学有所帮助吧~
缘起
目前的项目需要搭建一个搭建一个多用户MIMO-OFDM上行链路的系统(当然不只是基本的系统,多的和这个问题没多大关系,就不说了),并且在其中应用AI对其中的部分模块进行深度学习训练,或者对多模块进行联合优化。
我们知道MATLAB中有5g对应的toolbox,安装后拥有丰富的库函数实现5gnr链路级仿真的各个功能。(当然我们也尝试过sionna,但是部分模块感觉总有点问题,而且他是用tensorflow写的,有点反人类。)因此,我们非AI的基线使用MATLAB写成。
但我们的项目中需要“深度学习”的加入,而MATLAB对深度学习的支持还不是非常的完善。所以我们选用Pytorch进行部分“黑盒/半黑盒”网络的训练。
于是,如何将Pytorch中训练好的网络同MATLAB搭建好的系统就是一个大问题!
下面首先介绍一下“Python和MATLAB协同操作的方式”,接着叙述一下目前采取的方式和其中的坑。
协同方式
首先介绍一下,Python和MATLAB协同操作的方式,主要包含两大类:
- Matlab应用于Python——即在Python函数中调用MATLAB代码
- Python应用于Matlab——即在MATLAB中调用已经训练好的tensorflow/pytorch/onnx
Matlab应用于Python
两种思路
- 在python中使用
matlab.engine,即使用MATLAB Engine API for Python,实际上调用matlab本身。 - 将matlab函数单独打包为python库进行安装,即使用MATLAB Compiler SDK,实际上调用matlab runtime。
但是两者存在至关重要的区别
- MATLAB Engine API for Python 允许使用工作区(workspace),而 MATLAB Compiler SDK for Python 没有。因此,不能使用 MATLAB Compiler SDK for Python 调用 MATLAB 类(句柄)
- 而我们的代码中存在大量的matlab类,如解码等
因此目前主要考虑使用MATLAB Engine API,其基本使用方法如文档所示,matlab R2022a只支持Python 2.7/3.8/3.9。目前已基本测试能够在python中完成目前SIP的非AI系统matlab代码中的模块,且结果正确。后续迁移过程中,只是需要一定的数据类型转换。
目前主要存在的问题是,不论是调用matlab.engine还是使用Compiler SDK,在python看来,matlab代码部分类似于一个黑盒,无法实施反向传播,还没有找到很好的解决方式。
两个例子
nrULSCHDecoder_llr——MATLAB句柄(类)
-
engine API(类里面的function带点的不能用,需要在method中定义新函数以改变内部的property,.m文件需在同一文件夹下)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13import matlab.engine
import scipy.io as sio
L_emap111 = sio.loadmat('D:/MATLAB_drive/5g_local/Baseline/sip_qpsk_449/nrULSCHDecoder_llr/for_redistribution_files_only/L_Emap.mat')['L_emap111']
L_emap111=matlab.double(L_emap111.tolist())
eng = matlab.engine.start_matlab()
decodeULSCH = eng.nrULSCHDecoder_llr()
eng.setTargetCodeRate(decodeULSCH,0.587890625,nargout=0)
eng.setLDPCDecodingAlgorithm(decodeULSCH,'Belief propagation',nargout=0)
eng.setMaximumLDPCIterationCount(decodeULSCH,40,nargout=0)
eng.setTransportBlockLength(decodeULSCH,2976,nargout=0)
a = eng.step(decodeULSCH,L_emap111,'QPSK',1,0,nargout=4)
print(a[0].size) -
Compiler SDK——不支持
nrEqualizeMMSE_iter——MATLAB函数
- engine API
1 | import scipy.io as sio |
- Compiler SDK
1 | import nrEqualizeMMSE_iter |
Python应用于Matlab
基本的思路有三种,但各有利弊:
- Using models created in MATLAB using Deep Learning Toolbox™
- Converting models from other frameworks into MATLAB
- Co-executing models from other frameworks with MATLAB
例如matlab也提供了通信中的CSINet将Tensorflow框架和Matlab框架协同处理的方式,但matlab在其中的功能也仅是生成信道和仿真,matlab并未牵涉到反向传播的问题。
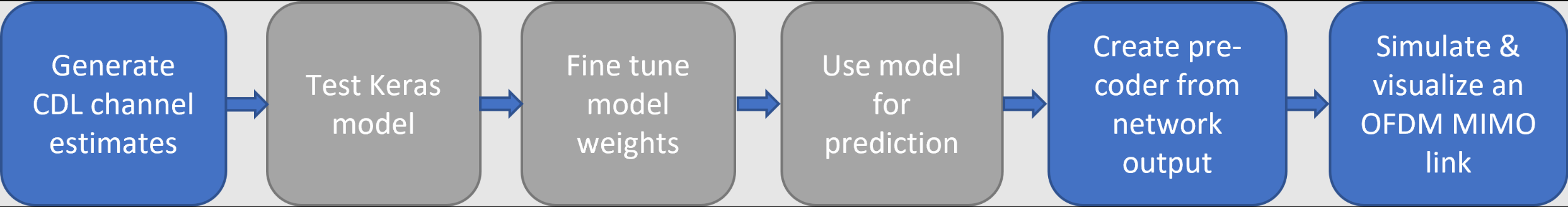
所以将python应用于matlab的方法,实际上和matlab应用于python存在类似的问题。
我也尝试将Pytorch训练好的网络,利用MATLAB r2023a中的库进行迁移,但是中途报错了,那个错误我也看不太懂,5555,所以这条路我们也弃用了!
目前采取的方式和其中的坑
目前采用的方式是利用Python,采用engine api的方式重写之前MATLAB整体的系统,并将Pytorch训练好的网络嵌入进该系统中。
——是的,我们还是没法对matlab函数进行反向传播。
——但是不要慌,重写不是从头开始,我们只是把大体框架用Python来写,其中复杂的打个包作为matlab函数调用就好了。
安装matlab engine api
-
按照matlab的要求在你的本地电脑或是服务器上安装“MATLAB”本体,如何在服务器上安装matlab,建议找学长(逃,我也不会,学长搞了好久)。
-
在对应的python环境中安装matlabengineforpython,具体可以参考这个。(其实就相当于给Python安装了一个库),
conda list后出现这个基本上就是安装好了1
matlabengineforpython R2022a pypi_0 pypi
利用engine api方式将matlab主函数改写为python主函数
-
使用engine api最基础的几个步骤就是:调用库、开启引擎、退出引擎
1
2
3import matlab.engine
eng = matlab.engine.start_matlab()
eng.quit() -
那么,我们需要把我们所有调用到的自己写的函数统统都放在主函数同一文件夹下吗?我之前是这么做的,但我问了问全知全能的new bing,他告诉我这样做就可以把函数目录添加到matlab路径中了,果然很好用!
1
2
3
4import os
folder_path = os.path.join(os.getcwd(), '../matlab_test')
eng.addpath(folder_path)
eng.rmpath(folder_path) -
【matlab句柄的改写】建议直接建一个Python类与之相对应
-
【matlab结构体数组的改写】直接给一个实例吧,*我也忘了当时怎么想的了,反正成功了!*没记错的话,是利用matlab输出数量不确定的函数的方式化解了结构体数组无法从matlab传播给Python的问题。
-
原始的函数
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72function channels = hMultiUserChannels(delayProfile,delaySpread,maximumDopplerShift,bsAntSize,ueAntSizes)
% Create empty output structures
numUEs = size(ueAntSizes,1);
channels = repmat(struct('channel',[],'chInfo',[],'pathFilters',[]),1,numUEs);
% Create a CDL channel model object configured with the desired delay
% profile, delay spread and Doppler frequency
channel = nrCDLChannel;
channel.DelayProfile = delayProfile;
channel.DelaySpread = delaySpread;
channel.MaximumDopplerShift = maximumDopplerShift;
channel.CarrierFrequency = 2.6e9;
channel.SampleRate = 7680000;
% Set the base station antenna array size. Initially, the channel
% operates in the UL direction, therefore the transmit antenna array
% corresponds to the base station, while the receive antenna array
% corresponds to the UE
channel.ReceiveAntennaArray.Size = [bsAntSize 1 1];
% Configure channel filtering:
% * For ChannelFiltering = true, the transmit resource grid will be
% OFDM modulated, filtered by the channel impulse repsonse, and
% OFDM demodulated to produce the receive resource grid
% * For ChannelFiltering = false, the channel will be applied to the
% transmit resource grid in the frequency domain to produce the
% receive resource grid
% ChannelFiltering = false is faster, at the expense of not modelling
% channel variation (and loss of orthogonality) due to Doppler across
% the duration of each OFDM symbol
channel.ChannelFiltering = false;
% Configure a set of azimuth and zenith angle offsets, used to adjust
% the angles of departure of the channel for each UE. This simulates
% the effect of different UEs being in different locations in the
% environment around the base station
% Azimuth offsets: assume a 120 degree wide sector, offset values
% are spread between (-60,60)
offsetsAoD = (rand([1 numUEs])-0.5) * 120;
% Elevation offsets: assume a tower height of 30m above the UE and
% cell radius of 600m, with UEs between 150m and 600m from the cell
% centre
range = 150 + (rand([1 numUEs]) * 450);
offsetsZoD = atand(30 ./ range);
% For each UE
for ue = 1:numUEs
% Create a copy of the original channel
cdl = copyCDL(channel);
% Set the UE antenna array size
cdl.TransmitAntennaArray.Size = [ueAntSizes(ue,:) 1 1];
% Configure the channel seed based on the UE number
% (results in independent fading for each UE)
cdl.Seed = 73 + (ue - 1);
% Configure the azimuth and zenith angle offsets for this UE
cdl.AnglesAoD(:) = cdl.AnglesAoD(:) + offsetsAoD(ue);
cdl.AnglesZoD(:) = cdl.AnglesZoD(:) + offsetsZoD(ue);
% Record the channel object and channel information in the output
channels(ue).channel = cdl;
channels(ue).chInfo = info(cdl);
end
end -
改写后的函数
matlab中函数改写:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75function varargout = hMultiUserChannels_py(delayProfile,delaySpread,maximumDopplerShift,bsAntSize,ueAntSizes,numUEs)
% Create empty output structures
numUEs = numUEs;
channels = repmat(struct('channel',[],'chInfo',[],'pathFilters',[]),1,numUEs);
varargout = cell(1, numUEs);
% Create a CDL channel model object configured with the desired delay
% profile, delay spread and Doppler frequency
channel = nrCDLChannel;
channel.DelayProfile = delayProfile;
channel.DelaySpread = delaySpread;
channel.MaximumDopplerShift = maximumDopplerShift;
channel.CarrierFrequency = 2.6e9;
channel.SampleRate = 7680000;
% Set the base station antenna array size. Initially, the channel
% operates in the UL direction, therefore the transmit antenna array
% corresponds to the base station, while the receive antenna array
% corresponds to the UE
channel.ReceiveAntennaArray.Size = [bsAntSize 1 1];
% Configure channel filtering:
% * For ChannelFiltering = true, the transmit resource grid will be
% OFDM modulated, filtered by the channel impulse repsonse, and
% OFDM demodulated to produce the receive resource grid
% * For ChannelFiltering = false, the channel will be applied to the
% transmit resource grid in the frequency domain to produce the
% receive resource grid
% ChannelFiltering = false is faster, at the expense of not modelling
% channel variation (and loss of orthogonality) due to Doppler across
% the duration of each OFDM symbol
channel.ChannelFiltering = false;
% Configure a set of azimuth and zenith angle offsets, used to adjust
% the angles of departure of the channel for each UE. This simulates
% the effect of different UEs being in different locations in the
% environment around the base station
% Azimuth offsets: assume a 120 degree wide sector, offset values
% are spread between (-60,60)
offsetsAoD = (rand([1 numUEs])-0.5) * 120;
% Elevation offsets: assume a tower height of 30m above the UE and
% cell radius of 600m, with UEs between 150m and 600m from the cell
% centre
range = 150 + (rand([1 numUEs]) * 450);
offsetsZoD = atand(30 ./ range);
% For each UE
for ue = 1:numUEs
varargout{ue} = struct('channel',[],'chInfo',[],'pathFilters',[]);
% Create a copy of the original channel
cdl = copyCDL(channel);
% Set the UE antenna array size
cdl.TransmitAntennaArray.Size = [ueAntSizes(ue,:) 1 1];
% Configure the channel seed based on the UE number
% (results in independent fading for each UE)
cdl.Seed = 73 + (ue - 1);
% Configure the azimuth and zenith angle offsets for this UE
cdl.AnglesAoD(:) = cdl.AnglesAoD(:) + offsetsAoD(ue);
cdl.AnglesZoD(:) = cdl.AnglesZoD(:) + offsetsZoD(ue);
% Record the channel object and channel information in the output
channels(ue).channel = cdl;
varargout{ue}.channel = channels(ue).channel;
channels(ue).chInfo = info(cdl);
varargout{ue}.chInfo = channels(ue).chInfo;
end
endPython中调用:
1
2
3
4simParaChannels = []
temp = eng.hMultiUserChannels_py(simPara.delayProfile, simPara.delaySpread, simPara.maximumDopplerShift, matlab.double(simPara.bsAntSize), matlab.double(simPara.ueAntSize),matlab.double(simPara.numUe),nargout=simPara.numUe)
for ue in range(simPara.numUe):
simParaChannels.append(temp[ue])
-
-
【函数和句柄类的改写】参考第二部分
-
【数据的转换】从 Python 中调用 MATLAB - MATLAB & Simulink - MathWorks 中国,可以参考下面这几个文档,其实最常用的就是把list转换为matlab数组格式
matlab.double(XXX),复数的话记得变成matlab.double(XXX, is_complex=True),如果你之前是numpy格式,那么需要先变成list(r2023a貌似不需要这一步了),即matlab.double(XXX.tolist(), is_complex=True),如果是cuda上torch的tensor的话那就再加一步XXX.cpu().detach().numpy()。
![image-20230404212334542]()
技巧和坑
- 【大坑】matlab和Python的行列排列顺序不同,reshape格外注意!!!
- 【小坑】注意matlab有多个输出时,需要加上l类似
nargout=3这样的选项。 - 【小坑】如果想把python类传给matlab作为matlab句柄类,里面的数据中不能出现numpy格式(r2023a可能没有这个问题了),请在需要回传给matlab的类中使用list存储数据。
- 【技巧】一些懒得改写的matlab代码(如自己也搞不清维度的reshape,各种matlab库函数的操作),其实可以自行封装成一个函数,直接调用你封装的函数即可
- 【技巧】matlab.double类型数组转化成numpy格式,直接
np.array(XXX, dtype=np.complex64) - 【技巧】numpy官方提供了matlab入门numpy用法的指南,改写可以参考NumPy for MATLAB users — NumPy v1.23 Manual
- 【最大的技巧】勤问new bing! 真的很强,甚至可以帮你改写代码!
最后,感谢new bing给我这篇文章的各种帮助!!!

